What do you know about volcanoes? Discuss the causes and effects of volcanic eruption.
 |
| What do you know about volcanoes? Discuss the causes and effects of volcanic eruption. |
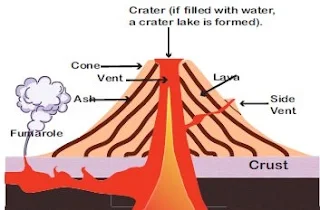
Volcanoes are geological features that form when magma, gas,
and other volcanic materials reach the Earth's surface through cracks and
openings in the Earth's crust. These eruptions can be both destructive and
beneficial, playing a significant role in shaping the Earth's landscape and
influencing the planet's climate.
Causes
of Volcanic Eruptions:
1. Magma Movement: The primary cause of volcanic
eruptions is the movement of magma from the Earth's mantle to the surface. This
magma is generated by the partial melting of rocks in the Earth's crust and
upper mantle.
2. Tectonic Plate Boundaries: Volcanoes are commonly found at
tectonic plate boundaries, where plates interact with one another. The most
common types are subduction zones, where one tectonic plate sinks beneath
another, and divergent boundaries, where plates move away from each other,
allowing magma to rise and form new crust.
3. Hotspots: Some volcanoes are not located at
plate boundaries but instead form over mantle plumes known as hotspots. These
plumes are stationary upwellings of hot material from the Earth's mantle that
can create volcanoes as tectonic plates move over them.
4. Pressure and Gas Buildup: As magma rises towards the surface,
pressure builds up within the volcano. Additionally, dissolved gases (such as
water vapor, carbon dioxide, and sulfur dioxide) in the magma expand as it
nears the surface, contributing to the explosive nature of some eruptions.
Effects
of Volcanic Eruptions:
1. Lava Flows: When magma reaches the surface, it
can flow as lava, spreading over the surrounding area and cooling to form new
rock. Lava flows can destroy everything in their path but can also create
fertile soil that supports plant growth over time.
2. Pyroclastic Flows: Explosive eruptions can generate
pyroclastic flows, which are a mixture of hot gases, ash, and volcanic
fragments that race down the volcano's slopes at high speeds. These flows are
extremely hazardous and can devastate large areas.
3. Ash and Tephra: Volcanic ash and tephra (small rock
fragments) can be ejected into the atmosphere during eruptions and may travel
over vast distances. These particles can damage aircraft, disrupt ecosystems,
and affect climate by reflecting sunlight and reducing temperatures.
4. Lahars: A lahar is a volcanic mudflow
formed when loose volcanic material mixes with water, often from melting snow
and ice during an eruption. Lahars can be highly destructive as they travel
downhill, impacting settlements and infrastructure.
5. Volcanic Gases: Volcanic eruptions release various
gases, including sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide, which can contribute to air
pollution and have significant effects on the atmosphere and climate.
6. Climate Impact: Massive volcanic eruptions can
inject large amounts of ash and gas into the atmosphere, leading to short-term
cooling of the Earth's surface. This phenomenon, known as volcanic winter, can
disrupt global weather patterns and have significant climatic consequences.
Overall, volcanic eruptions are essential natural processes
that shape the Earth's crust, create new landforms, and contribute to the
planet's geological and ecological diversity. While they can have devastating
effects on local and global scales, they also play a crucial role in the
Earth's dynamic systems.
